Venipuncture
Goals
The goal of venipuncture is to obtain blood for evaluation of biochemical and biophysical information concerning the physiology of the patient. This procedure provides basic theory and procedure for performing simple venipuncture by evacuated system, syringe and needle, and butterfly needle for the purpose of blood collection.
Background
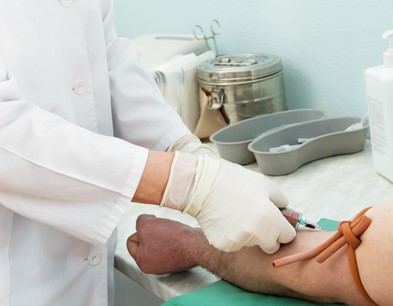 Venipuncture is a technique whereby a vein is entered by a sharp rigid stylet or by a needle. Phlebotomy is the process of entering the vein to remove blood.
Venipuncture is a technique whereby a vein is entered by a sharp rigid stylet or by a needle. Phlebotomy is the process of entering the vein to remove blood.
Contraindications
The following are relatively common difficulties encountered when selecting a suitable vein. In some cases, the affected site should be avoided; in others, special techniques are required.
Avoid the following sites if possible:
- Scars
Scarred veins are difficult to palpate and penetrate. They may have impaired circulation and therefore yield erroneous results. Scars may be present due to repeated phlebotomy procedures or IV drug use. - Burns
Healed burn areas may be scarred, whereas fresh burns are very painful and susceptible to infection. - Tattoos
Tattoos should be avoided if possible. Tattooed areas may contain dyes that interfere with testing, have impaired circulation, and may be more susceptible to infection. - Mastectomy
Venipuncture should be avoided on the same side as the radical mastectomy (total breast and lymph node removal). Due to the disruption of lymph circulation (lymphostasis), test results may be erroneous. Lymphostasis also makes the patient more prone to infection and swelling. Tourniquet application should be avoided as it may cause injury. In the event of a bilateral mastectomy or no available veins, an alternative site such as the feet or ankle may be used or a capillary puncture (dependant on the type of sample amount of testing). Alternatively you may consider performing the venipuncture without the use of a tourniquet. Generally the side with the most recent mastectomy is avoided. - Arteriovenous shunt (AV shunt) or fistula
An AV fistula is the surgical fusion of a vein and an artery. Fistulas are reserved for dialysis procedures. Never apply a tourniquet or perform a venipuncture on an arm with an AV shunt. - Hematoma
The area has a disrupted vessel network, so the blood specimen from this area may be contaminated with interstitial fluid and/or bilirubin. If another vein is not available, collect the specimen below the hematoma. The area may also be painful, resulting in patient discomfort. - Edema
This impairs circulation and therefore may affect test results. The tissue may also be fragile and damage from the tourniquet can result.
Alter the technique for the following:
- Thin, fragile veins
These are usually best entered using a small gauge needle (22g) and a small syringe. The aspiration pressure can then be controlled by pulling back on the plunger slowly. Alternatively, a butterfly needle with a syringe gives good results. - Surface veins
Immobilize carefully as these tend to be poorly secured in connective tissue and therefore roll or move ahead of the needle hampering penetration. Lower the angle of needle entry to prevent going through the vein. - Deep veins
Usually deep veins cannot be seen, but careful palpation will show their location and direction. Increase the needle angle to penetrate more deeply. - Veins that run across the arm
Position the needle so that it follows the direction of the vein, not across the vein. - Intravenous (IV) therapy
Blood should not be drawn from an arm with an IV running unless there is no other available site. The IV fluid can contaminate the specimen, causing erroneous results. If there is no other site, always draw the sample BELOW the IV site if possible.- Use a different vein than the one containing the IV
- Collect 5 mL of blood and discard before collecting sample
- Write on the requisition/draw sheet that the sample was collected from an arm with IV running and what the IV solution consists of
- Most protocols for this collection will require that the IV should be shut off for at least two minutes before the collection

